Insurance Industry: Navigating Matching Adjustment Reforms PS10/24 with Scorable
The Matching Adjustment (MA) under Solvency II enables insurers to adjust the valuation of their liabilities by holding long-term assets with predictable cash flows that match these liabilities. This structure helps reduce balance sheet volatility and lowers capital requirements, fostering more strategic investment capabilities. Recent reforms from the Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) now aim to enhance this framework, providing insurers with broader flexibility to diversify and optimize portfolios.
Heightened Expectations for Internal Credit Ratings
A critical component of the updated MA framework is an increased emphasis on internal credit ratings. Insurers holding internally rated assets are now required to examine and strengthen the robustness, maturity, and capacity of their internal rating frameworks. This scrutiny is geared toward ensuring that internal ratings are as reliable and granular as external credit ratings. As part of this process, firms must implement "notched" credit ratings—ratings that provide finer differentiation within each credit category—by the end of 2024. Notching, which involves assigning detailed ratings within each credit quality step, aims to capture even minor differences in credit quality, enhancing the risk sensitivity of insurers’ portfolios.
Reduced Capital Penalty for Sub-Investment-Grade Assets
A notable shift in the MA reforms is the reduced capital penalty for holding sub-investment-grade (SIG) assets (BB+ or below), removing the boundary often referred to as the “BBB cliff.” This relaxation could enable insurers to explore investments in emerging sectors, such as technology and ESG-focused projects, which might initially have lower credit ratings. While substantial allocations to SIG assets remain unlikely, selective exposure, managed prudently, could contribute to portfolio diversification and align with MA requirements.
However, the PRA mandates that firms demonstrate effective risk management systems for their SIG assets. Insurers holding SIG assets must be prepared to identify, measure, monitor, and manage these risks, and to meet the PRA’s guidelines for ongoing independent validation and external assurance.
Spotlight on MA PS10/24
Purpose: The MA under Solvency II lets insurers adjust liabilities by holding long-term assets with cash flows that align with these liabilities.
Benefits: Helps reduce balance sheet volatility and lowers capital requirements, supporting stable, strategic investment.
New Reforms: Recent PRA updates provide greater flexibility, enabling insurers to diversify and optimize their portfolios.
Focus Areas: Insurers must adopt rigorous internal credit rating frameworks and manage sub-investment-grade assets prudently.
Discover how Scorable’s real-time credit insights support your MA strategies
How Scorable Supports Portfolio Managers in Adapting to MA Reforms
Scorable, bondIT’s AI-powered credit analytics platform, provides indispensable tools for portfolio managers navigating the complexities of MA reforms. It enhances credit risk assessment, monitoring, and management by reducing reliance on manual processes. With independent, forward-looking insights, Scorable optimizes existing workflows and empowers decision-making across portfolios of all sizes. Here’s how Scorable makes a difference:
Advanced Credit Scoring and Monitoring
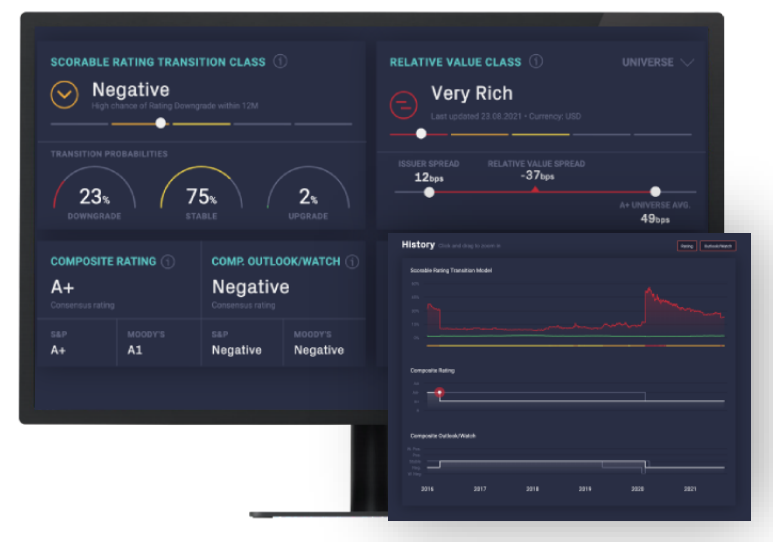
- Scorable leverages machine learning algorithms to provide real-time, AI-based credit scores that adapt to evolving market conditions.
- This dynamic scoring capability helps PMs identify high-quality assets with predictable cash flows that meet the requirements for inclusion in MA portfolios, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Scorable is unique in offering investors notch-level downgrade predictions.
Insight into Emerging Risks and Opportunities
- With its deep analytics capabilities, Scorable allows PMs to gain a granular understanding of credit risks, even for newly eligible asset classes under the updated MA framework.
- The platform's insights enable proactive risk management, helping PMs to identify potential threats to portfolio stability and capitalize on new investment opportunities.
- Whilst data-driven, Scorable is not a black box. Thanks to its Explainable AI, users can identify the drivers of changes in credit risk.
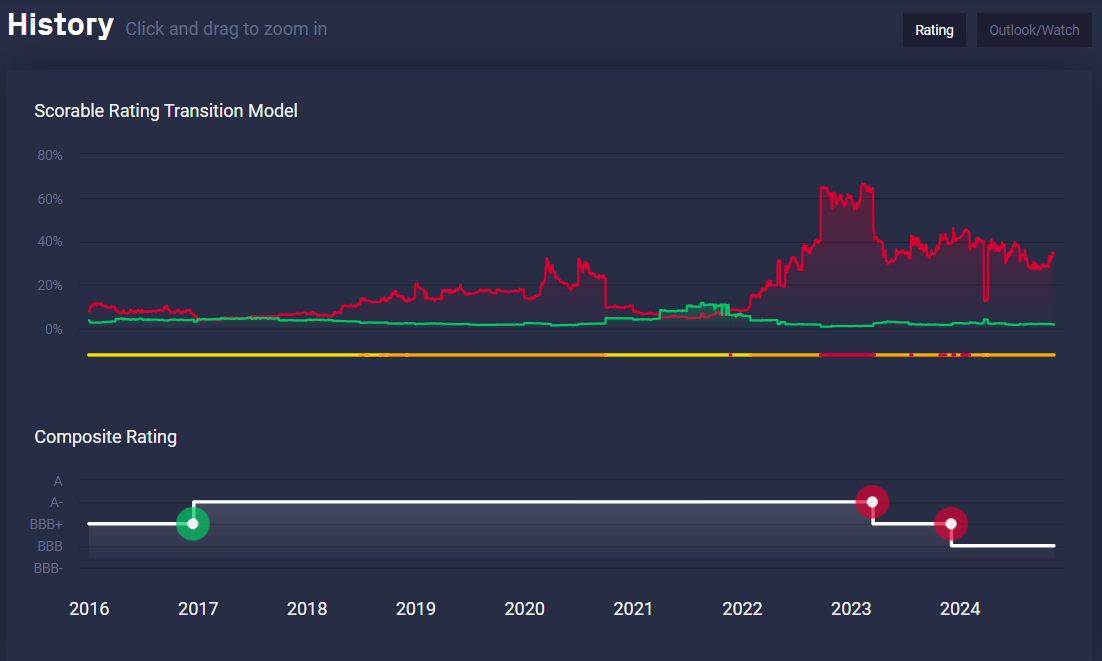
- Scorable's real-time alerts and updates enable PMs to quickly react to shifts in credit risk, ensuring that assets continue to meet the stringent requirements for inclusion in MA portfolios.
- Identify spread deviations with Scorable’s Relative Value feature.
Seamless Integration with Portfolio Strategies
- Scorable's analytics can be seamlessly integrated into existing portfolio construction and management processes, facilitating the alignment of investment strategies with the latest MA guidelines.
- By providing clear risk and return assessments, it supports PMs in building diversified portfolios that balance regulatory requirements with performance goals.
Identifying Outliers with Confidence
- Traditional signals like spreads and watchlists highlight potential risks but lack an objective framework for measuring downgrade likelihood.
- Scorable fills this gap by providing independent, forward-looking assessments that reduce manual intervention and enhance decision-making processes across portfolios.
Data-Driven Decision-Making for Regulatory Compliance
- Scorable's AI-driven insights empower portfolio managers to make informed, data-backed decisions when selecting assets for MA portfolios, ensuring alignment with newly defined risk parameters and Solvency II reforms.
- By integrating objective, instrument-level assessments, Scorable supports senior management in confirming that ratings reflect the totality of risk, as required for regulatory attestation.
- This streamlined, data-driven approach reduces the manual burden of credit risk monitoring, enabling insurers to adapt efficiently to ongoing regulatory changes while maintaining focus on strategic portfolio growth.
Get in touch today to discover how Scorable’s advanced analytics can streamline your compliance and risk management.
Scorable: Your Partner in the Evolving MA Landscape
The updated MA framework introduces both expanded investment opportunities and increased demands for rigorous internal credit assessments. Scorable’s advanced analytics and AI capabilities equip portfolio managers with the tools needed to navigate this shifting landscape confidently. With Scorable, PMs can adapt their strategies to tap into a broader investment universe while maintaining compliance and managing risk effectively.
